Increase your maximum power!
Whether at the final sprint or the last repetition in your workout. With the Heave Boys Creatine Powder, challenge the peak of your best performance!
The microfine Creatine Monohydrate Powder impresses without further additives and dissolves very well in fruit juice or water to bring you directly to the front. Creatine is an endogenous and completely natural substance produced by the body from the amino acids glycine, arginine and methionine in the liver, kidneys and pancreas. There are several forms of creatine – but the monohydrate is particularly easy for the body to absorb and is therefore the active ingredient in our 100% Pure Creatine. Use this advantage to increase your physical performance during training. For this reason the white gold is hardly to be excluded from every shelf for competitive and leisure sportsmen.
Every athlete has crystal clear advantages when supplementing creatine! Increase your maximum strength during your workout, increase your speed during intense endurance sessions. The 100% Pure Creatine is a real all-rounder and the congenial partner for everyone.
Heavy Boys 100% PURE CREATINE – ACHIEVE YOUR GOALS
100% Pure Creatine is the best choice for supporting the following goals:
Power gain
More intensive training sessions
Preserve musculature
Faster regeneration
CREA-BOOST
Strong energy reserves
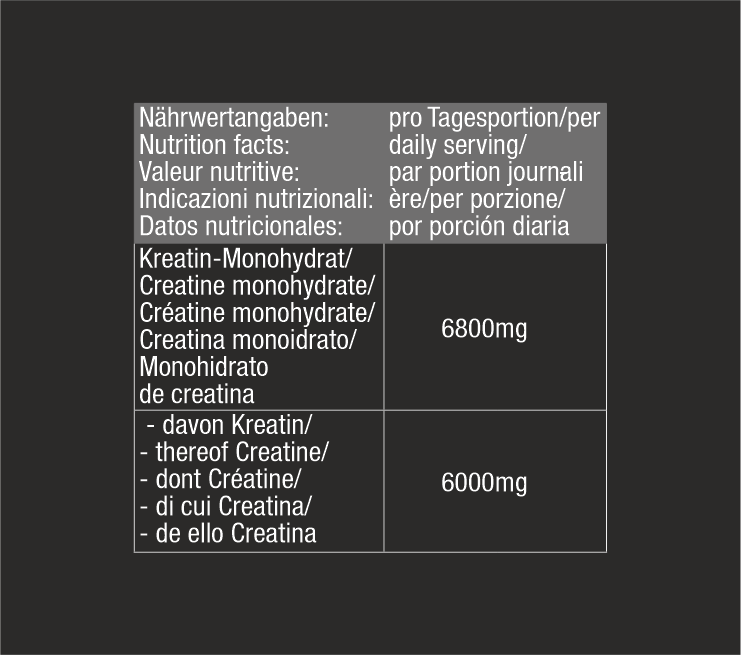
Did you know that creatine is available during your training as a short-term energy reserve for extreme efforts? For example, you can set new personal records during a workout. Creatine accumulates in the muscle and serves there as a quick energy reserve, so it is directly at hand when you need more energy in the short term to move heavy weights or complete a sprint. You should supplement daily one portion, about 5g, to keep this memory permanently filled.
CREATINE – A DEFINITION
Creatine is an acid which is principally found in meat. Creatine is mainly stored in the human skeletal muscles and can partially be produced by the body itself. Other sources which can supply the body with creatine are fish and meat (especially beef). Natural sources of creatine frequently have a high fat content, which means consideration should be given to its consumption. In addition, the body can take in concentrated creatine in the form of nutritional supplements which are low in fat. Creatine can increase physical performance during dynamic strength training in the course of brief and intense workouts. Athletes can also undergo a creatine regimen or take creatine in combination with other products.
INFORMATION ON CREATINE REGIMES
Because storage in the body is limited, a creatine supplement regimen is often recommended. After taking supplements of an average 3 g per day over a short eight to twelve week period, have a break of at least one month in order to prevent a tolerance effect. However, some creatine products can be taken over longer periods, providing they are only taken immediately prior to physical exertion in order to improve training performance. Our bodies independently produce around one to two grammes of creatine per day. An average man weighing around 70 kg has about 120 gramme creatine distributed over the entire musculature.
FUNCTIONS IN THE BODY
95 % of creatine is found in the musculature. Besides protein and other important nutrients, creatine is also found in the Health Claims Regulation. In this regulation on nutritional and health claims on food labelling, the following function has been awarded to creatine: “Creatine increases physical performance during short-term, high intensity, repeated exercise bouts.” (Health Claims Regulation, 2012) But it`s not only the performance-enhancing properties of creatine which allow it to stand out from the crowd, the many and varied dosage forms also play a role. The advantage of creatine in powder form is how easy it is to mix into protein shakes or fruit juice. There are hardly any differences in the effects of the different creatine forms. So, when selecting the right creatine product, its important to consider personal preference on the way it is to be taken. Athletes who are constantly on the go, often prefer capsule products as these are more convenient to take than powder. So-called Creatine Monohydrate, however, is often cheaper.
INFORMATION ON INTAKE
The question of intake or administration is a very interesting one, especially for athletes, as they need to estimate how much additional creatine the body needs. The body can create creatine itself. The body creates creatine from the amino acids Arginine, Glycine and Methionine. The conversion process mainly takes place in the kidneys, liver and pancreas. In this way, the body creates around 1 g creatine per day. However, the average requirement is about 3 g creatine per day. This means that in order to cover its needs, the body needs to have an additional creatine supply beside the creatine produced by the body.
The body gets this additional creatine through food. Creatine is primarily found in meat and fish. This requirement can be quite a bit higher in athletes than in non-athletes. Since sources of creatine frequently contain lots of fat, it is difficult to get an adequate supply. However, there are specific nutritional supplements that can help ensure an adequate, low-fat supply of creatine.